This article describes how to use the report modeling interface to edit models and how to build a temporary report.
The main topics in this article are as follows:
To access the report modeling interface:
On the main ReportWORQ sidebar, select the Reporting Models icon.
.png)
A tree list of reporting models appears.
Navigate to the model you want to edit and open it for editing.
The Fields view appears..png)
Previewing Data
When you preview data, you can control the number of rows displayed and whether the data is queried from the datasource or retrieved from cache.
To preview data:
Select Preview.
.png)
Data rows appear..png)
If you want to change Preview settings for future preview requests, do the following:
Open the Preview Row Limit dialog.

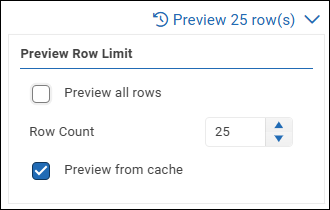
If you want to change the number of data rows displayed, specify the Row Count or select Preview all rows.
If you want ReportWORQ to query the datasource each time a preview is requested, clear the Preview from cache check box.
Tip: Previewing data from cache reduces the volume of queries sent to the datasource, and the preview may render more quickly.Close the dialog.

The changed settings will apply the next time a preview is requested.
When you are finished previewing data, select Edit to return to the previous view.

Selecting and Adding Fields
You can select fields to include in the model. By default, all fields are included.
You can also add new fields, to be either mapped to fields from the datasource, or left unmapped so report authors can populate them via Excel formulas.
To select or deselect fields:
In the Fields view, select the Field Selections button.
The Edit Field Selections dialog appears.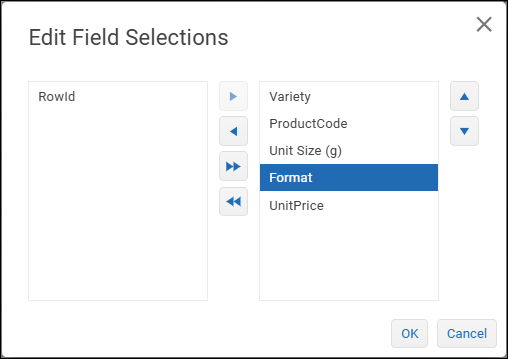
The right side lists fields that are included in the model. The left side lists fields that are not included.Move fields between the two sides as required:
Double arrow buttons move all the fields.
Single arrow buttons move the selected field only.
Select OK.
To add a new field:
In the Fields view, select the Add Field button.
The Field Name dialog appears.Provide a name for the new field, and then select OK.
The field is added to the Fields list.Do one of the following:
If you want to map the new field to a datasource field, in the Mapped Field box, select the data field that contains data you want to use for the new field.
If you want to leave the field unmapped so report authors can populate it via an Excel formula, in the Mapped Field box, select Unmapped.
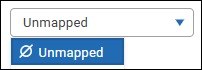
Defining Report Filters
Report filters are a set of grouped data filters. Only data that satisfies all filters is made available to report authors.
The set of report filters contains one or more filter groups, each of which contains one or more field filters. A logical operator (And or Or) is applied within each filter group. Another logical operator is applied to the overall set of groups.
Tip: Filters can also be applied as field properties of individual fields.
To define report filters:
Select the Report Filters button.
The Edit Report Filters dialog appears.
Tip: A dashed rectangle outlines each group of filters.From the Add Field list, select a field you want to filter.
A filter expression box appears. The field name appears above it.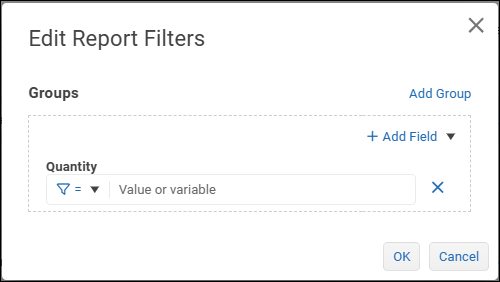
Define the first filter expression by selecting a comparison operator and specifying a test value.
In the following example, the filter requires the data value to be greater than or equal to 5..png)
If the test value is text, enclose it in single quotes as shown below:
The test value can be a variable. To declare a variable, enclose the{{variable name}}in double curly braces. In the following example, the test value is a variable named myVar.
If the filter group requires additional filter expressions, select Add Field and then select a logical operator at the top of the filter group:
And — Data must satisfy all filter expressions in the group.
Or — Data must satisfy one or more filter expressions in the group.
Define additional filter expressions within the group as required.
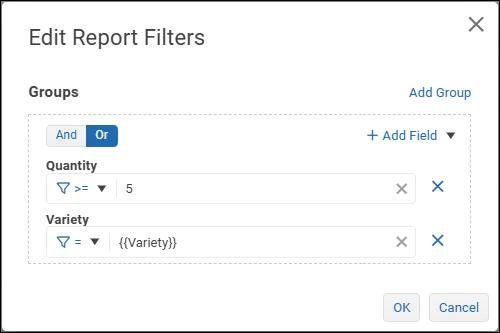
If the filter set requires another group of filters:
Select Add Group and then, at the top of the filter editor, select a logical operator to apply to the set of groups.

And — Data must satisfy all groups.
Or — Data must satisfy one or more groups.
Within the new group, define filter expressions and select a logical operator if the group contains multiple expressions.
Continue to add and define filter groups as required.
The following example has two groups.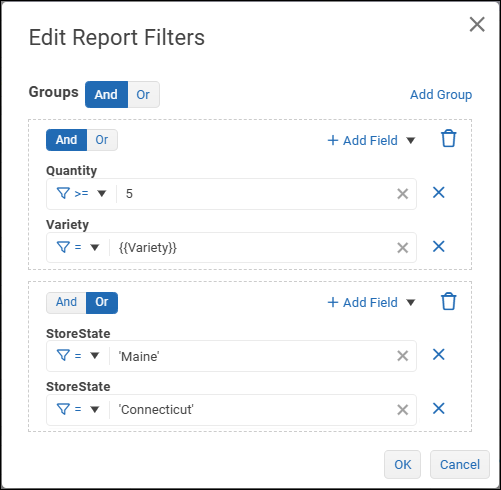
When you are finished defining the filter set, select OK.
The filter editor closes.
Above the Fields list, the Report Filters icon is dark to indicate that report filters are defined.
Editing Field Properties
The Fields view contains metadata about each data field in the model.
.png)
IMPORTANT: After you configure field properties, select Save Changes.
Field properties are as follows:
Visible — Shows or hides the field in the model. Hidden fields can still be referenced in queries.
The open eye icon.png) indicates that the field is visible to report authors.
indicates that the field is visible to report authors.
The closed eye icon indicates that the field is not visible to report authors.
indicates that the field is not visible to report authors.Id — The unique identifier for the field.
Name — The name of the field, as it will appear to report authors. We recommend using names that clearly identify the contents and purpose of the field. If your model includes two identically named fields, rename them to avoid confusion.
Mapped Field — The datasource field that provides the data.
Type — The data type of the field. Not editable.
Sample Value — An example of a data value for the field. Sample values demonstrate the nature of the data the field may contain.
Status — Indicates whether settings for the field are valid.
 — Unknown status.
— Unknown status.
To validate the model and update the status of all fields, select Validate..png) — Field settings are valid.
— Field settings are valid..png) — Field settings are not valid.
— Field settings are not valid.
 Trash Can icon — Permanently deletes the field from the model.
Trash Can icon — Permanently deletes the field from the model. Filter icon — Opens the filter editor.
Filter icon — Opens the filter editor.
Tip: Filters can also be applied at the report level. Only data that satisfies all filters is made available to report authors.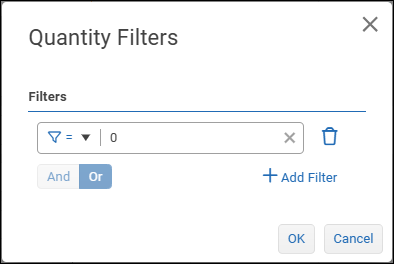
To define a field-level filter set:Define the first filter expression by selecting a comparison operator and specifying a test value.
In the following example, the filter requires the data value to be greater than or equal to 5..png)
If the test value is text, enclose it in single quotes as shown below:
The test value can be a variable. In the following example, the test value is a variable named myVar.
If additional filter expressions are required, select Add Filter and then select a logical operator:
And — Data must satisfy all filter expressions in the set.
Or — Data must satisfy one or more filter expressions in the set.
Define additional filter expressions as required.
When you are finished defining the filter set, select OK.
The filter editor closes.
In the Fields list, the filter icon for the field is dark to indicate that filters are defined.
Configuring Options
The Options pane contains additional settings related to the model.
.png)
Tip: If the Options pane is collapsed, expand it. ![]()

To configure options:
In the Variables area of the Options pane:
Refresh the list of variables.


If any variables are listed, provide values for them. The values you specify become defaults.
Tip: If a variable value is text, enclose it in single quotes. For example, 'Maine'.
Building a Report
You can build a temporary report in the report modeling interface, using many of the same tools report authors use in the ReportWORQ add-in for Excel. Building and viewing Report may help you confirm that a model contains all the data fields that report authors require.
Report building includes configuring column options and report options. Column options apply to the selected column, while report options apply to the overall report. If the same option can be set at the column level and the report level, the column-level setting takes precedence.
Note: The report cannot be exported or added to ReportWORQ Jobs. It exists only during the current modeling session and is not saved.
This section includes the following topics:
To access the report building interface:
Select Build a Report.

The Columns list appears. In the following example, the model has six columns.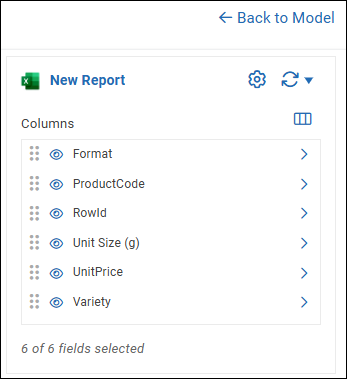
Tip: To close the report builder, select Back to Model.If you want to switch to the Report Options view, select the gear icon.

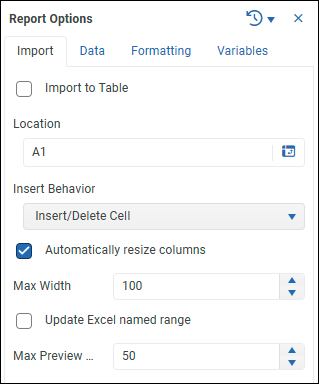
Tip: To switch to the Columns list, close the Report Options view.
Refreshing the Report
You can refresh the report from cached data or from source data.
To refresh the report:
Near the top of the interface, expand the refresh menu and select a refresh option:
 Refresh from source — Queries the underlying datasource for fresh data and then renders the report.
Refresh from source — Queries the underlying datasource for fresh data and then renders the report.
Tip: The first time you refresh the report, this is the only available option. Refresh from cached data — Renders the report based on data from the most recent query. This option reduces the volume of queries sent to the datasource, and the report may render more quickly.
Refresh from cached data — Renders the report based on data from the most recent query. This option reduces the volume of queries sent to the datasource, and the report may render more quickly.
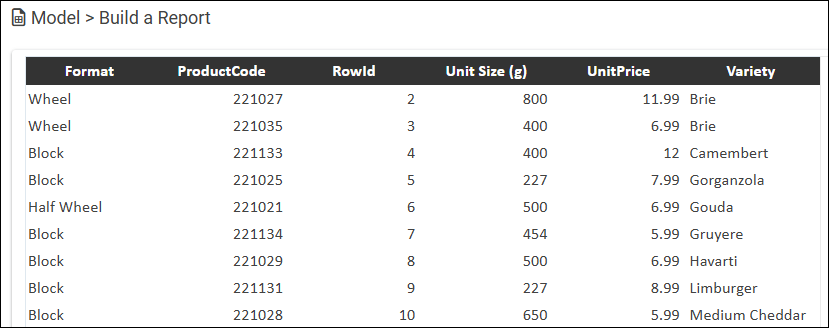
The following figure shows a refreshed report.
Choosing Fields for the Report
You can choose which fields from the underlying data model are available to be later included as columns in the report. Choosing only the required fields reduces the volume of queries sent to the underlying datasource and improves performance.
To choose fields:
Above the Columns list, select the fields icon.
.png)
The Choose Fields list appears.
Select the fields you need for the report. This includes visible fields as well as hidden fields required for filter queries.
Close the Choose Fields list (x) to return to the Columns list.
Editing Column Options
Column options define which columns and data appear in the report, and the visual appearance of each column’s contents.
The figure below shows the Columns list for a report named Products.
.png)
Selecting and Reordering Columns
You can select which columns appear in the report and arrange the order of the columns.
To select columns:
Select the columns you want to display in the report.
The open eye icon.png) indicates that the column is included.
indicates that the column is included.
The closed eye icon indicates that the column is excluded.
indicates that the column is excluded.
Note: Hidden columns are still available for filter references.
To reorder columns:
Hover over the dots
 beside a column that you want to move.
beside a column that you want to move.
The drag icon appears.Select and drag the column to the desired position in the list.
Formatting Columns
Each column is formatted individually. Format options include:
Header options — Header text, grouping, and sectioning.
Data options — Sorting, aggregating, and filtering data.
Formatting options — Visual appearance of headers, data, and subtotals.
To access the format options for a column:
In the Columns list, select the arrow to the right of the column name.
.png)
Format Options appear on three tabs (Header, Data, and Formatting).
Header Options
The Header tab contains the following options:
Display Mode — Enables you to group or section data based on the current column. You can set grouping and sectioning on multiple columns in the same report.
The options are as follows:None — The report is not modified.
Group — Where the data value for the current column is identical in multiple consecutive rows, only one instance of the value is displayed.
In the following example, the Group display mode is applied to the Format column.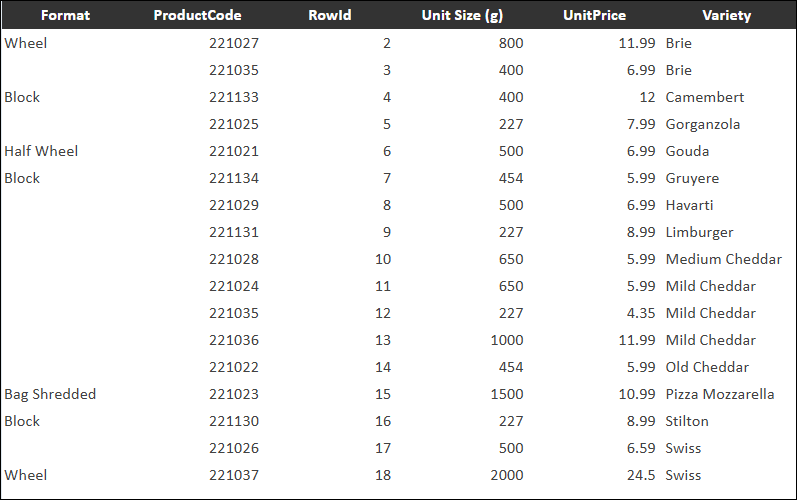
Tip: To vertically center the values upon which the groups are based, select Merge grouped cells.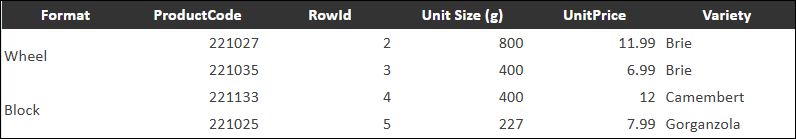
Tip: You can sort the current column so that for each data value, all rows that have that value are displayed together, as shown below. Sort Mode options are available on the Data tab.Section — The report preview is divided into sections based on values from the current column. All rows that contain a given value are displayed in one section. In the following example, the Section display mode is applied to the Format column.
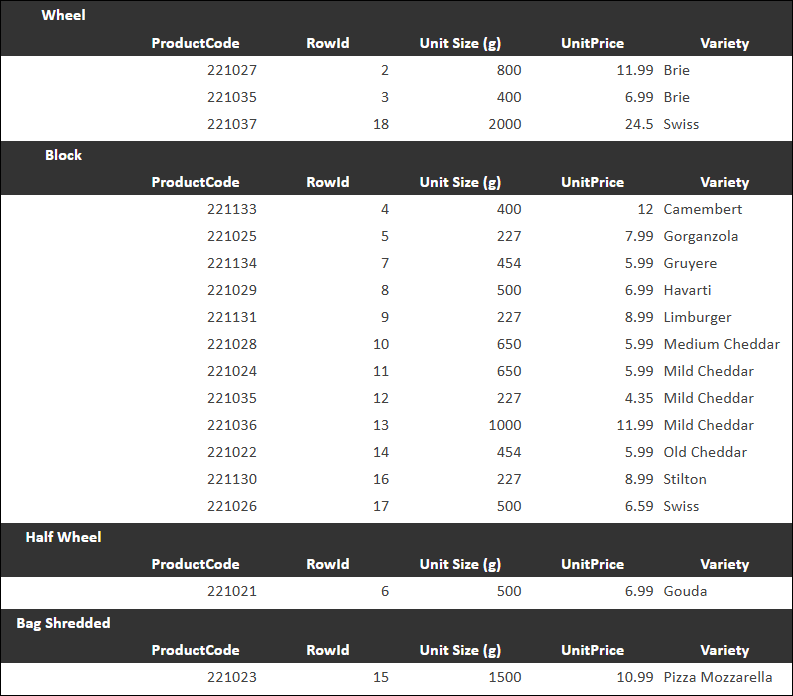
When you section a column, additional Layout options appear:
Layout options are as follows:Display section in separate column — Current column values, upon which the sections are based, are displayed in a separate column. When not selected, they are displayed above the first column.
Merge cells in section row — Displays the values for the sectioned column above their sections. In the following example, the Format column is sectioned, resulting in sections for Wheel and Block.
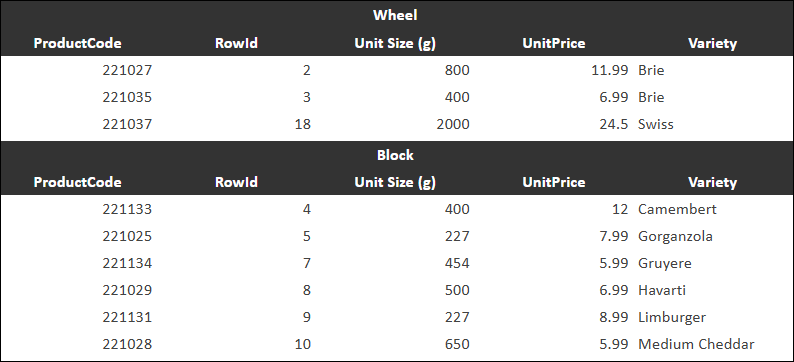
Show totals for aggregate fields — Enables the display of aggregate values for columns that have aggregation configured. Aggregate options are available on the Data tab.
If any columns in the report preview are grouped or sectioned, they must be configured to show totals for aggregate fields, on the Header tab of their column options.
On the Data tab of the report options, the Show totals for aggregate fields option must be selected.Auto outline section — Renders each section as a collapsible group of rows.
Insert blank row — Inserts a blank row between sections.
Insert page break — Inserts a page break between sections.
Header — Enables you to define the header text.
Data Options
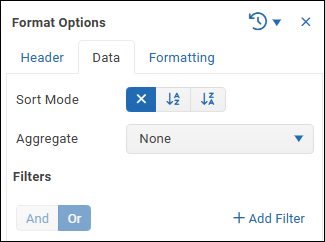
The Data tab contains the following options:
Sort Mode — Enables you to sort rows based on the current column.
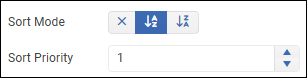
If you want to apply nested sorting to multiple columns, set the Sort Priority for each sorted column. Lower numbered sorting takes precedence. Do not assign the same sort priority to multiple columns.Aggregate — Enables you to aggregate data values for the current column.
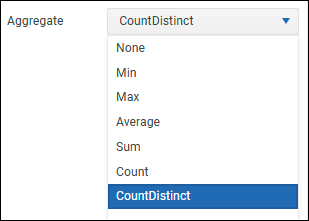
Aggregate options are as follows:None — Values are not aggregated.
Min — The lowest value is displayed. Applies to numerical values only.
Max — The highest value is displayed. Applies to numerical values only.
Average — The average value is displayed. Applies to numerical values only.
Sum — All values are added, and the result is displayed. Applies to numerical values only.
Count — Displays the total number of values, including repeated values. Applies to text values only.
Count Distinct — Displays the number of unique values. Applies to text values only.
Filters — Enables you to define data filters for the current column. Rows that do not meet all filter criteria are excluded from the report.
Tip: You can also define a set of filters at the report level, on the Data tab of Report Options.
To define filters for the current column:
Select Add Filter.
Define the first filter expression by selecting a comparison operator and specifying a test value.
In the following example, the filter requires the data value to be greater than or equal to 5..png)
If the test value is text, enclose it in single quotes as shown below:
The test value can be a variable. In the following example, the test value is a variable named myVar.
If additional filter expressions are required, select Add Filter and then select a logical operator:
And — Data must satisfy all filter expressions in the set.
Or — Data must satisfy one or more filter expressions in the set.
Define additional filter expressions as required.
Formatting Options
The Formatting tab enables you to define the visual appearance of cells for the current column.
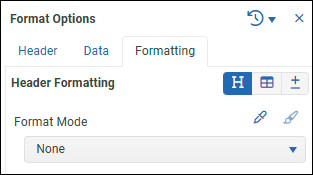
To format column contents:
Select an icon to select what type of cells to configure:
 — Header cells
— Header cells — Data cells
— Data cells — Subtotal cells
— Subtotal cells
From the Format Mode list, select one of the following:
None — No formatting is applied to the column.
Inherit — Formatting is inherited from the report-level format options.
Automatic — Standard ReportWORQ formatting.
Cell Based — Any Excel formatting you apply to a cell of the selected cell type within the column will be applied to all cells of that type.
For example, if you are formatting data cells, you can apply formatting to one data cell and when you refresh the report, all data cells in the column will be formatted to match.Basic — Enables you define formatting using tools that appear within the add-in, as shown below:
.png)
Style — Applies formatting based on a named style from Excel.
Range — Applies formatting to match the formatting of cells in the specified cell range.
Editing Report Options
Report options apply to the overall report, rather than individual columns. For options that can be set at both the report level and at the column level, the column level settings override those set at the report level.
To access report options:
From the Columns view, select the Report Settings icon.

The Report Options area consists of four tabs (Import, Data, Formatting, and Variables).
Note: Options on the Import tab are not applicable for reports built in the report modeling interface.
Data Tab
The Data tab enables you to control what data appears in the report.
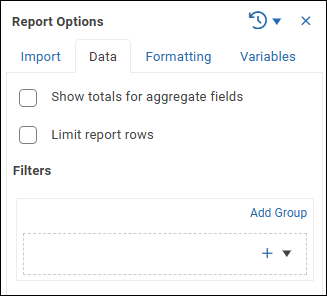
Data tab options are as follows:
Show totals for aggregate fields — Enables aggregate totals to be displayed in the report. Aggregate totals can be displayed only for columns that are configured to calculate aggregates, on the Data tab of their Column Options. If any columns in the report are grouped or sectioned, they must also be configured to show totals for aggregate fields, on the Header tab of their Column Options.
Limit report rows — Sets the maximum number of rows rendered when the report runs as part of a ReportWORQ Job.
Filters — Enables you to define a set of grouped data filters at the report level. Rows that do not meet all filter criteria are excluded from reports.

Tip: You can also define filters for individual columns, on the Data tab of their Column Options.
To define report-level filters:
In the Filters area of the Data tab, expand the + list and select a column you want to filter.
A filter expression box appears. The field name appears above it.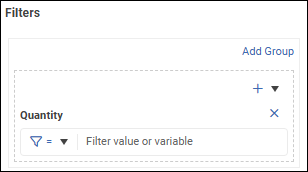
Tip: A dashed rectangle outlines each group of filters.Define the first filter expression by selecting a comparison operator and specifying a test value.
In the following example, the filter requires the data value to be greater than or equal to 5..png)
If the test value is text, enclose it in single quotes as shown below:
The test value can be a variable. To declare a variable, enclose the{{variable name}}in double curly braces. In the following example, the test value is a variable named myVar.
If the filter group requires additional filter expressions, expand the + list and select a column, then select a logical operator at the top of the filter group:
And — Data must satisfy all filter expressions in the group.
Or — Data must satisfy one or more filter expressions in the group.
Define additional filter expressions within the group as required.
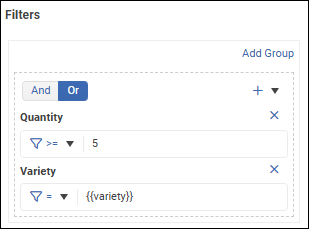
If the filter set requires another group of filters:
Select Add Group and then, at the top of the filter editor, select a logical operator to apply to the set of groups:

And — Data must satisfy all groups.
Or — Data must satisfy one or more groups.
Within the new group, define filter expressions and select a logical operator if the group contains multiple expressions.
Continue to add and define filter groups as required.
The following example has two groups.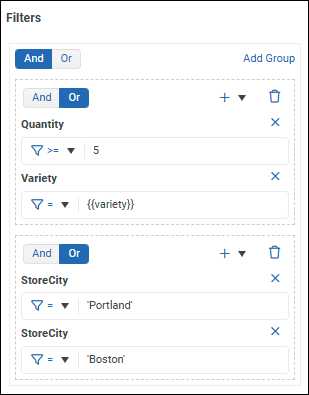
Formatting Tab
The Formatting tab enables you to define the default visual appearance of cells in the report. These defaults can be overridden by individual column formats.
.png)
To format report contents:
Select an icon to select the type of cells to configure:
 — Header cells
— Header cells — Data cells
— Data cells — Subtotal cells
— Subtotal cells
From the Format Mode list, select one of the following:
None — No formatting defaults are applied.
Automatic — Standard ReportWORQ formatting.
Cell Based — Any Excel formatting you apply to a cell of the selected cell type within the report will be applied to all cells of that type.
For example, if you are formatting data cells, you can apply formatting to one data cell and when you refresh the report, all data cells in the report will be formatted to match.Basic — Enables you define formatting using tools that appear within the add-in, as shown below:
.png)
Style — Applies formatting based on a named style from Excel.
Range — Applies formatting to match the formatting of cells in the specified cell range.
Variables Tab
The Variables tab lists all ReportWORQ variables applicable to the report.
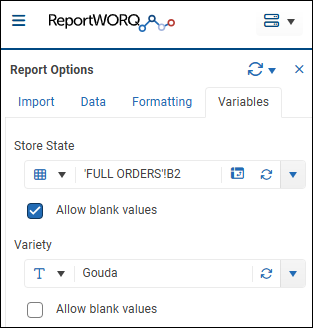
Each variable is part of a filter definition for a filter applied at the report level, the column level, or in the underlying reporting model. Only data that satisfies all filters is included in the report output.
Note: All variables must be assigned values in order to run the report or refresh the report.
To assign a value to a variable:
From the list, select Text as the type of variable value.
Type the text in the box.
Clear or select the Allow blank values checkbox:
Clear — A variable value must be provided here.
Selected — If no variable value is provided here, the default value from the underlying reporting model is used.